| Tikalon Blog is now in archive mode.
An easily printed and saved version of this article, and a link
to a directory of all articles, can be found below: |
|
This article |
| Directory of all articles |
Rare Earth Shortage
June 21, 2010
The
rare earth elements are
scandium,
yttrium, and the fifteen
lanthanides. I've worked with nearly all of these elements
over the years in some interesting hydrogen storage and magnetic materials; and as
phosphors. They are not really that rare. Some of them are as abundant
copper and
lead. The most rare,
thulium and
lutetium, are more than a hundred times more abundant than
gold. Their rarity stems more from the difficulty in extracting the metals from their ores, and the fact that even these ores are found in just a few locations. Since most differ only in the number of
f-shell electrons, they are chemically very similar and are difficult to separate.
China, produces about 95 % of the world's rare earth elements, and the US imports most of its rare earth elements. In the period 2005-2008, the US imported 91% of its rare earths from China, 3% from France, 3% from Japan, and 3% from other sources [1]. The rare earths are useful in many advanced materials, including
permanent magnets used in small motors and actuators, so it's significant that China intends to limit its rare earth exports. [2, 3] Although China may require these elements for its own industries, it's more likely that it wants to maintain a high price for such materials during the economic downturn.
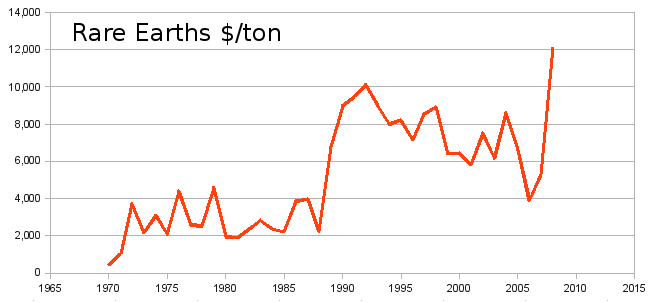
Rare Earth Prices, 1970-2008. Data from Ref. 1.
Materials scientists are inventive people, so alternative compositions may be developed to give desired properties without rare earth elements. One such possibility is using
nanomaterial structures and compositions [3]. Another option is to get your rare earths elsewhere. The US has huge reserves of rare earth ores that have not been exploited because of cost [4]. The
US Geological Survey estimates that US rare earth reserves are about thirteen million metric tons, compared with the 2009 worldwide production of 124,000 metric tons [4]. Known deposits include one at Lehmi Pass, at the border between Idaho and Montana; another at Diamond Creek, Idaho. These sites are owned by a company called
U.S. Rare Earths.
Molycorp Minerals has a mine for the lighter rare earths, such as
lanthanum and
neodymium, at
Mountain Pass, California. The interesting thing is that Molycorp sends its ores to China for final processing [4]. A separation plant for industrial-scale rare earth refining is an expensive proposition, costing up to a billion dollars. No such plant exists in the US, and it would take eight years to build [4]. As
Macbeth said, "If it were done, when 'tis done, then 'twer well, it were done quickly." [5]
References:
- Rare Earths - Statistics and Information USGS 2010 (PDF File).
- Dexter Johnson, "Can Nanotechnology Provide Relief in Rare Earth Resource Squeeze?" IEEE Spectrum Online (June 8, 2010).
- Dipankar De Sarkar, "Rare earth revolutionary," Hindustan Times UK (May 29, 2010).
- Jeremy Hsu, "U.S. sits on rare supply of tech-crucial minerals," MSNBC Online (March. 9, 2010).
- Macbeth by William Shakespeare (Project Gutenberg).
Permanent Link to this article