Miniature Antennas
October 2, 2017
One of my first
electronic circuits, built when I was a
7th grade student, was a
VLF (Very Low Frequency) radio receiver. It was constructed from a few
transistors to detect
lightning strikes, and also the
natural radio waves known as
atmospherics at those
frequencies. It would also register signals when a large
electric motor was activated in the
neighborhood. The signals were connected to an
amplifier and monitored on a
loudspeaker. The sounds, greatly enhanced in the
morning and called the
dawn chorus, were a lot like the communications from
extraterrestrials heard in
"B" movies.
The circuit was described in an article in an electronics
hobby magazine, likely
Popular Electronics. Only simple and inexpensive circuits could be presented in such a magazine, and the simplicity of this circuit was a consequence of the VLF radio signals being in the
audio frequency band, accessible by any home
hi-fi equipment. The inexpensive feature in my case was a consequence of an electronic
technician neighbor who donated many of the
electronic components.
The
antenna used in this radio receiver was a long length of
wire. I later learned that this was a very
inefficient antenna for VLF signals, since
simple antennas like this should be as long as about a quarter
wavelength of the signal. There's a very useful
equation for conversion of frequency
f to wavelength
λ using the
speed of light c (3.00 x 10
8 meter/second),
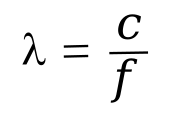
![]()
Putting an
audio frequency of 10,000
Hz into this equation, knowing that a
hertz has dimensions of 1/second, gives a wavelength of 30
kilometers (18.64
miles)! My antenna was obviously a very inefficient collector of radio
energy at VLF frequencies.
As I explained in an
earlier article (Robert A. Helliwell, June 16, 2011), VLF pioneer and discoverer of the atmospheric radio signals known as
whistlers,
Robert A. Helliwell, actually built a thirteen mile long antenna. Not only that, but it was built at
Antarctica in a location called Siple Station that was active from 1971-1988.[1] The antenna was used to
transmit VLF radio signals into
Earth's magnetosphere, to be detected half a world away in
Canada.
Antenna size has always been a problem for designers of
mobile devices. Fortunately, the demand for greater
data rates has forced the migration of
cellphone communication to higher and higher frequencies.
Cellular frequencies started at 450
MHz and 800-900 MHz, and have climbed to 1,800-1,900 MHz, and future devices might operate at 2,500 MHz. The following table shows the wavelengths for these frequencies. The lower wavelengths allow efficient antennas to be included in today's cellphones.
| Frequency (MHz) |
Wavelength (Meters) |
| 450 |
0.67 |
| 800 |
0.38 |
| 900 |
0.33 |
| 1,800 |
0.17 |
| 1,900 |
0.16 |
| 2,500 |
0.12 |
Semiconductor technology can be used to fabricate extremely small devices, and these could be used in many applications, including
in vivo medical sensing. However, getting these devices to communicate their data wirelessly is a problem, since the allowed antenna dimensions are much smaller than a radio wavelength.
That's the problem addressed in an
open access article by a large
research team from
Northeastern University (Boston, Massachusetts),
Westford Academy (Westford, Massachusetts),
Andover High School (Andover, Massachusetts), and the
Air Force Research Laboratory (
Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Dayton, Ohio).[2-4]
The minimum practical size for an antenna is about a tenth of the wavelength.[2] As
Nian Sun, a
professor of
Electrical and Computer Engineering at Northeastern and corresponding author of the study,
"A lot of people have tried hard to reduce the size of antennas. This has been an open challenge for the whole society... We looked into this problem and thought, why don't we use a new mechanism?"[4]
The new mechanism involves the use of a
resonance medium with a
wave propagation speed much smaller than the speed of light. Acoustic waves in
solids propagate at a speed of just a few thousand
meters per second, so their wavelength is smaller by five
orders of magnitude at a given frequency.[2-3] They were able to transition from the
electromagnetic realm to the
acoustical realm by developing acoustically-actuated,
nanomechanical,
magnetoelectric (ME) antennas.[2]
Their ME antennas are fabricated as suspended
ferromagnetic-
piezoelectric thin-film heterostructures that transmit and receive radio waves through the ME effect at their acoustic resonance frequencies.[2] In transmission, the
bulk acoustic waves in the ME antennas stimulate magnetic
oscillations in the magnetic thin film, and these oscillations produce electromagnetic radiation. Conversely, in radio reception, the ME antennas convert the magnetic fields of electromagnetic waves to acoustic waves using the
piezoelectric effect.[2]
The concept for this type of antenna was
theoretically proposed in 2015.[5] When the excitation was via
surface acoustic waves, such devices only worked at a few kilohertz. The antennas of the present study are based on bulk acoustic waves, and they perform as well as conventional antennas, but at a hundred times smaller size.[2] The concept was demonstrated at at
VHF and
UHF frequencies.[2]
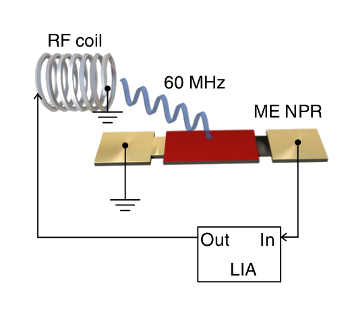
An acoustically-actuated, nanomechanical, magnetoelectric antenna operating at the VHF frequency of 60 MHz.
The frequency of operation is low enough that analysis could be done by resonance assisted by a high frequency lock-in amplifier (LIA) feeding an induction coil.
Fig. 1a from Ref. 2, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The antennas are fabricated as thin sheets of a
piezomagnetic material, the magnetic
analog to a piezoelectric material that expands and contracts in response to a
magnetic fields to convert an incident electromagnetic wave to acoustic waves via the magnetic component of the electromagnetic wave.[2-3] The piezomagnetic material in the devices is an
alloy of
iron,
gallium, and
boron.[3] A piezoelectric material then converts these acoustical waves to an oscillating
voltage. That handles the radio reception. For transmission, a voltage produces vibrations in the piezoelectric, and these are coupled to the piezomagnetic to produce electromagnetic waves.[2-3]
The research team demonstrated the concept with two kinds of acoustic antennas, one having a
rectangular membrane for reception of VHF signals, and the other having a
circular membrane for frequencies in the
gigahertz range. A comparison of the disc antenna with a conventional
loop antenna of the same size showed that 2.5 gigahertz signals were transmitted and received about 100,000 times more
efficiently.[3]
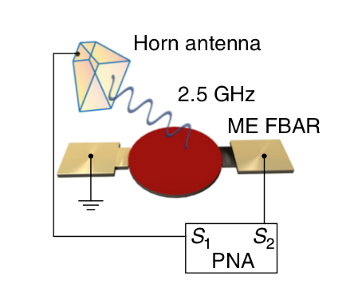
An acoustically-actuated, nanomechanical, magnetoelectric antenna operating at the UHF frequency of 2.5 GHz.
In this case, excitation was with a horn antenna, and analysis was done with a parametric network analyzer (PNA).
Fig. 3a from Ref. 2, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
There are many novel applications for such miniature antennas, such as
in vivo medical sensors that could even be
implanted in the
brain.[3] One potential problem is the high
energy density of the antennas, which would heat surrounding
tissue,[3] but this effect might also be put to use in
hyperthermia therapy, as in killing
cancer cells. There are also possible
security issues, since these antennas would make it easier to create small "
bugs" for covert intelligence-gathering. Going back to the VLF theme at the start of this article, Sun and his team is creating kilohertz-frequency antennas that are room-sized, rather than miles long.[3]
References:
- Melissae Fellet, "Robert Helliwell, Radioscience and Magnetosphere Expert, Dead at 90," Stanford Report, May 20, 2011.
- Tianxiang Nan, Hwaider Lin, Yuan Gao, Alexei Matyushov, Guoliang Yu, Huaihao Chen, Neville Sun, Shengjun Wei, Zhiguang Wang, Menghui Li, Xinjun Wang, Amine Belkessam, Rongdi Guo, Brian Chen, James Zhou, Zhenyun Qian, Yu Hui, Matteo Rinaldi, Michael E. McConney, Brandon M. Howe, Zhongqiang Hu, John G. Jones, Gail J. Brown, and Nian Xiang Sun, "Acoustically actuated ultra-compact NEMS magnetoelectric antennas," Nature Communications, vol 8, Article no. 296, August 22, 2017, doi:10.1038/s41467-017-00343-8. This is an open access article with a PDF file available here
- Matthew Hutson, "Mini-antennas could power brain-computer interfaces, medical devices," Science, August 22, 2017.
- Allie Nicodemo, "When it comes to antennas, size matters," Northeastern University Press Release, August 23, 2017.
- Zhi Yao, Yuanxun Ethan Wang, Scott Keller, and Gregory P. Carman, "Bulk acoustic wave-mediated multiferroic antennas: architecture and performance bound," IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag., vol. 63, no. 8 (August, 2015), pp. 3335-3344.
Linked Keywords: Electronic circuit; 7th grade student; VLF (Very Low Frequency); radio receiver; transistor; lightning strike; nature; natural; radio wave; radio atmospheric; frequency; electric motor; neighborhood; amplifier; loudspeaker; morning; dawn chorus; extraterrestrials in fiction; "B" movie; hobby; magazine; Popular Electronics; audio frequency band; high fidelity; hi-fi equipment; technician; electronic component; antenna; wire; energy conversion efficiency; inefficient; monopole antenna; wavelength; equation; speed of light; hertz; Hz; kilometer; mile; energy; whistler (radio); Robert A. Helliwell; Antarctica; transmitter; transmit; Earth's magnetosphere; Canada; mobile device; data rate; mobile phone; cellphone; communication; cellular frequencies; MHz; semiconductor; technology; in vivo; medicine; medical; sensor; sensing; open-access journal; open access article; research; Northeastern University (Boston, Massachusetts); Westford Academy (Westford, Massachusetts); Andover High School (Andover, Massachusetts); Air Force Research Laboratory; Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Dayton, Ohio; Nian Sun; professor; Electrical and Computer Engineering at Northeastern; resonance; velocity factor; wave propagation speed; solid; meters per second; orders of magnitude; electromagnetism; electromagnetic; acoustics; acoustical; nanoelectromechanical system; nanomechanical; magnetoelectric effect; ferromagnetism; ferromagnetic; piezoelectricity; piezoelectric; coating; thin-film; heterostructure; volume; bulk; oscillation; piezoelectric effect; theory; theoretical; surface acoustic wave; very high frequency; VHF; ultra high frequency; UHF; analysis; resonance; lock-in amplifier; inductor; induction coil; Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License; material; analogy; analog; magnetic field; alloy; iron; gallium; boron; voltage; rectangle; rectangular; membrane; circle; circular; gigahertz; loop antenna; energy conversion efficiency; efficient; GHz; horn antenna; two-port network; parametric; network analyzer (electrical); implant (medicine); brain; energy density; tissue; hyperthermia therapy; cancer cell; computer security; security issue; covert listening device; bug.