Nature Abhors Quasicrystals
January 16, 2012
The
idiom that "Nature abhors a vacuum" is attributed to
Baruch Spinoza, who developed a lot of interesting ideas that were certainly well ahead of his
seventeenth century milieu. Scientists have the
vacuum under control, both
experimentally and
theoretically, but what nature really abhors is
crystals with
five-fold symmetry.
The reason for this is that space can't be filled with
dodecahedrons, which are
regular polyhedra with
pentagonal sides.
Johannes Kepler, in his book,
Harmonices Mundi, showed that even when you drop down a
dimension, pentagons are anathema. You can't fill a plane with regular pentagons, although
irregular pentagons will do the job.
The dodecahedron is one of the five
Platonic solids, which are those solids that can be formed using the same regular polygon as faces. The others are the
tetrahedron,
cube,
octahedron and
icosahedron.
Aristotle, in his book,
On the Heavens, stated that the tetrahedron can fill space, but he was wrong.

Platonic solid sculptures in Steinfurt, Germany. (Photo by Zumthie, via Wikimedia Commons).
The only Platonic solid that can fill space is the cube. If we relax our polyhedron requirement to solids that are formed through combinations of any regular polyhedra, not just one type, we get the
Archimedean solids. Four objects in this class join the cube as space filling polyhedra. These are the
triangular prism,
hexagonal prism,
truncated octahedron and
gyrobifastigium.[1] Gyrobifastigium? I thought that
mathematicians only drank coffee, but that's more like a
beer pong word.
When atoms arrange themselves in crystals, they necessarily fill space, and they do this in the simplest way possible by ordering themselves into small polyhedral cells that repeat. Not surprisingly, the majority of crystal cells are
cubic and hexagonal crystals. Looking at the first series of transition metals,
scandium through
zinc, we have four
hexagonal crystals, four
body-centered cubic crystals, and two
face-centered cubic crystals.
As I summarized in a
previous article (The 2011 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, October 7, 2011), no one believed
Dan Shechtman in 1982 when he found five-fold symmetry in an
alloy of
aluminum that contained fourteen atomic percent
manganese.[2-3] The material was novel, since it was formed by
rapid solidification, a technique that inhibits motion of
atoms as the material solidifies.
Shechtman's
electron diffraction data indicated an
icosahedral point group symmetry. Icosahedra can't fill space. Not surprisingly, it took two years for Shechtman to get his paper accepted for publication; but after Shechtman's publication, other scientists came forward with examples of the same thing.
In 1992 the
International Union of Crystallography changed its definition of a crystal from "a regularly ordered, repeating three-dimensional pattern" to a solid with a "discrete diffraction diagram."[4] Shechtman was vindicated in his award of the 2011
Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his discovery of these
quasicrystals, crystals that are ordered, but not periodic.
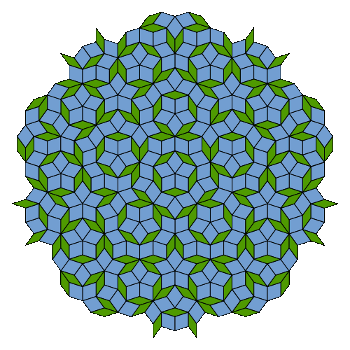
A rather pretty tiling with five-fold rotational symmetry. This is a Penrose tiling, named after the mathematicial physicist, Roger Penrose.
Penrose was issued a patent on his tiling in 1979.[5]
(Via Wikimedia Commons))
The unusual way that quasicrystalline materials were synthesized in the laboratory seemed to indicate that they would be impossible to find in nature. Then, in 2009, a team of scientists from
University of Florence (Florence, Italy),
Princeton University and
Harvard University, reported on the discovery of
micrometer-sized quasicrystalline grains of an alloy of aluminum,
copper, and
iron in a
mineral specimen from the
Koryak Mountains in
Siberia. It was not apparent how these crystals could have formed in nature.[6]
Members of that same research team have published a paper in the
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences that combines a little detective work with their usual science.[7-9] The detective work was because the
provenance of the mineral specimen was not that well established. It was in the collection of a
Florence museum, which bought it in 1990 from a private collector in
Amsterdam, along with thousands of others.[9]
The label on the specimen's box stated that the specimen came from the Koryak Mountains. Investigation found that the specimen was presumably smuggled from
Russia through
Romania. It was finally traced back to its originator, who had dug it from clay in a region of Russia at the
Bering Strait.[9]
Theoretical physicist,
Paul Steinhardt of Princeton University, and his colleagues have visited that region looking for more quasicrystal specimens, but the results of that trek have yet to be published.[9]
The small quasicrystals in the specimen are an icosahedrite phase of Al
63Cu
24Fe
13 that appear to have come from a
meteorite.[7] These crystals are in combination with many other mineral phases, including a grain of
stishovite, which is a phase of
silica that is formed only at very
high pressures (≥10
Gpa), likely through an impact.[7] Analysis of the
oxygen isotope concentrations also show a non-terrestrial origin like that of
carbonaceous chondrites.[8].
As the abstract of the PNAS paper summarizes,
"...Our evidence indicates that quasicrystals can form naturally under astrophysical conditions and remain stable over cosmic timescales, giving unique insights on their existence in nature and stability."[7]
References:
- Space-Filling Polyhedron on Mathworld.
- D. Shechtman, I. Blech, D. Gratias and J.W. Cahn, "Metallic phase with long range orientational order and no translation symmetry,", Physical Review Letters, vol. 53, no. 20 (November 12, 1984), pp. 1951-1953.
- D. Levine and R. Steinhardt, "Quasicrystals: a new class of ordered structures," Physical Review Letters, vol. 53, no. 26 (December 24, 1984), pp. 2477-2480.
- Kenneth Chan, "Israeli Scientist Wins Nobel Prize for Chemistry," The New York Times, October 5, 2011.
- Roger Penrose, "Set of tiles for covering a surface," US Patent No. 4,133,152, January 9, 1979.
- Luca Bindi, Paul J. Steinhardt, Nan Yao and Peter J. Lu, "Natural Quasicrystals," Science, vol. 324, no. 5932 (June 5, 2009), pp. 1306-1309.
- Luca Bindi, John M. Eiler, Yunbin Guan, Lincoln S. Hollister, Glenn MacPherson Paul J. Steinhardt and Nan Yao, "Evidence for the extraterrestrial origin of a natural quasicrystal," Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., doi: 10.1073/pnas.1111115109, January 3, 2012.
- Impossible crystals are 'from space', BBC News January 3, 2012.
- Richard Van Noorden, "The quasicrystal from outer space," Nature News, January 3, 2012.
Permanent Link to this article
Linked Keywords: Idiom; Baruch Spinoza; seventeenth century; vacuum; ultra-high vacuum; vacuum state; crystal; five-fold symmetry; dodecahedron; regular polyhedra; pentagon; Johannes Kepler; Harmonices Mundi; dimension; irregular pentagon; Platonic solid; tetrahedron; cube; octahedron; icosahedron; Aristotle; On the Heavens; Steinfurt, Germany; Zumthie; Wikimedia Commons; Archimedean solids; triangular prism; hexagonal prism; truncated octahedron; gyrobifastigium; mathematicians only drank coffee; beer pong; cubic; scandium; zinc; hexagonal crystals; body-centered cubic; face-centered cubic; Dan Shechtman; alloy; aluminum; manganese; rapid solidification; atom; electron diffraction; icosahedral symmetry; icosahedral point group symmetry; International Union of Crystallography; Nobel Prize in Chemistry; quasicrystal; Penrose tiling; mathematicial physicist; Roger Penrose; University of Florence (Florence, Italy); Princeton University; Harvard University; micrometer; copper; iron; mineral; Koryak Mountains; Siberia; Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences; provenance; Florence; Amsterdam; Russia; Romania; Bering Strait; theoretical physicist; Paul Steinhardt; meteorite; stishovite; silica; high pressure; Pascal; Gpa; oxygen isotope; carbonaceous chondrite; US Patent No. 4,133,152.